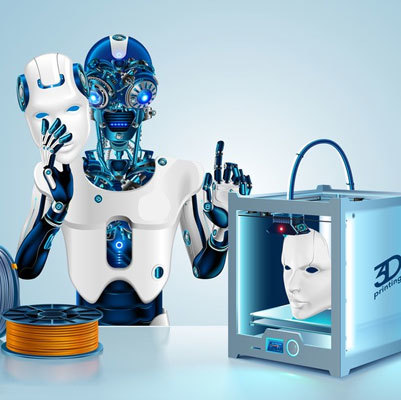
From Concept to Reality: How to Choose the Best 3D Printer for Your Projects
2025-05-28 11:00
From Concept to Reality: How to Choose the Best 3D Printer for Your Projects
Table of Contents
- Understanding 3D Printing Technology
- Types of 3D Printers: Which One is Right for You?
- Key Features to Consider When Choosing a 3D Printer
- Budgeting for Your 3D Printing Projects
- Materials and Filaments: Choosing the Best for Your Needs
- 3D Modeling and Software: Tools to Bring Your Ideas to Life
- Maintenance and Support: Ensuring Longevity
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
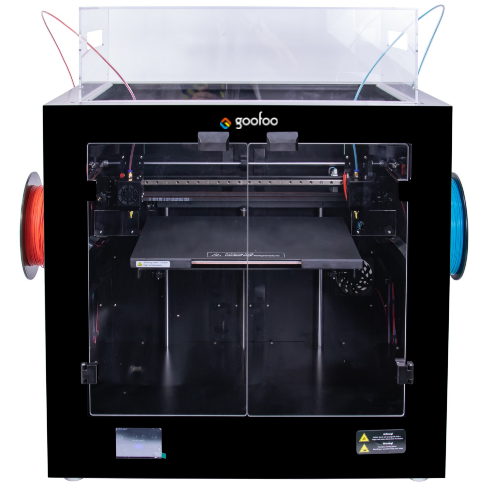
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that allows users to create three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This process involves layering materials, such as plastics or metals, to build intricate structures. **Understanding the basics of 3D printing** is crucial when evaluating which printer suits your projects best. The technology has evolved rapidly over the past decade, offering various printing methods that cater to different applications, from rapid prototyping to artistic creations.
Types of 3D Printers: Which One is Right for You?
Choosing the right type of 3D printer is essential for achieving your desired project outcomes. Here are the most common types of 3D printers:
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM printers are the most popular and widely used in the consumer market. They work by melting a filament and extruding it layer by layer to create an object. **FDM printers** are ideal for hobbyists and beginners due to their affordability and ease of use.
Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into a solid object, offering high precision and detail. They are often favored for applications requiring intricate designs, such as jewelry making or dental applications.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS printers use a laser to fuse powdered material into solid structures. This technology is effective for creating durable and complex geometries, making it a popular choice in engineering and industrial applications.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
DLP is similar to SLA but uses a digital light projector to cure resin in a layer at once. It provides rapid printing speeds and high-resolution outputs, catering well to the demands of creative professionals.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing a 3D Printer
When evaluating different 3D printers, consider these key features:
Build Volume
The **build volume** refers to the maximum size of the objects you can print. Assess your project needs to determine the appropriate dimensions that will accommodate your designs.
Print Resolution
Print resolution impacts the quality of the final product. Higher resolutions (measured in microns) yield finer details, which is particularly important for intricate designs.
Print Speed
Print speed is a significant factor, especially for projects with tight deadlines. Faster printers can save time but may compromise quality. Balancing speed and precision is essential.
Ease of Use
Consider the user-friendliness of the printer. Features like touchscreen interfaces, auto-calibration, and easy filament loading can make a significant difference, particularly for beginners.
Budgeting for Your 3D Printing Projects
**Budgeting** is crucial when selecting a 3D printer. Prices can vary significantly based on technology, brand, and features. Determine your budget range and explore options within that limit.
Don’t forget to account for additional costs, such as:
- Filaments or resins
- Replacement parts
- Software licenses
- Maintenance and repair services
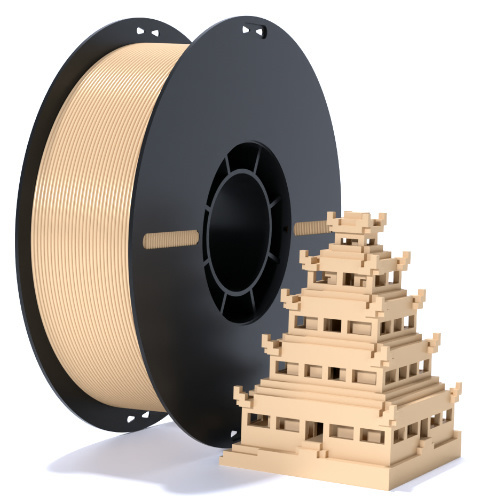
Materials and Filaments: Choosing the Best for Your Needs
The type of material you choose affects the strength, flexibility, and finish of your prints. Here are some common materials used in 3D printing:
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is a biodegradable plastic that is user-friendly and ideal for beginners. It’s available in a wide range of colors and is often used for prototypes and educational purposes.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a tough and durable plastic, making it suitable for functional parts. It requires a heated bed and proper ventilation due to its fumes.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG blends the best of both PLA and ABS, offering strength and ease of use. It’s also food-safe, making it a good option for household items.
Resins
For SLA printers, various resins are available, each serving different purposes—from standard resin for general use to specialty resins for high-detail or flexible prints.
3D Modeling and Software: Tools to Bring Your Ideas to Life
To create objects for 3D printing, you often need design software. Here are some popular options:
- Tinkercad: A user-friendly, browser-based application ideal for beginners.
- Fusion 360: A professional-grade CAD software for more complex designs.
- Blender: A powerful open-source tool suited for artistic and detailed modeling.
Maintenance and Support: Ensuring Longevity
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity of your 3D printer. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Keep the printer clean and free of debris.
- Regularly check and tighten loose parts.
- Perform software updates as needed.
Additionally, consider the availability of customer support and community resources for troubleshooting and advice.
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D printer for your projects involves careful consideration of various factors, including the type of printer, key features, materials, and your budget. By thoroughly assessing your options and aligning them with your project needs, you can move from concept to reality and unlock endless creative possibilities. Whether you are a hobbyist, engineer, or artist, investing in the right 3D printer will empower you to transform your ideas into tangible creations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much does a good 3D printer cost?
The cost of a reliable 3D printer can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the technology and features.
2. What materials can I use with my 3D printer?
Common materials include PLA, ABS, PETG, and various resins, each suited for different applications.
3. Do I need special software for 3D printing?
Yes, design software is necessary to create 3D models, which can then be sliced into instructions for the printer.
4. How long will it take to print an object?
Print times vary based on object size, complexity, and printer speed, ranging from minutes to several hours.
5. Can I upgrade my 3D printer later?
Many 3D printers allow for upgrades or modifications, including new extruders, print heads, or heated beds for enhanced performance.
This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for anyone looking to invest in a 3D printer, enhancing your understanding and helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your project requirements.
best 3d printer
Last
Prev
Recommended News
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Skype / WhatsApp: +86 592-5713513 / +86-13860126490
No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong'an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Xiamen Goofoo Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备2022008070号-1 SEO 300.cn
Phone:+0086 592-5713513
Address: No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong’an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Email: sales@goofoo3d.com
We will give you feedback in time