Transforming Ideas into Reality: The Magic of 3D Printing
2025-05-12 11:40
Transforming Ideas into Reality: The Magic of 3D Printing
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to 3D Printing
- 2. What is 3D Printing?
- 3. How Does 3D Printing Work?
- 4. Applications of 3D Printing Across Industries
- 5. Benefits of 3D Printing
- 6. Challenges Facing 3D Printing
- 7. The Future of 3D Printing
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. FAQs About 3D Printing
1. Introduction to 3D Printing
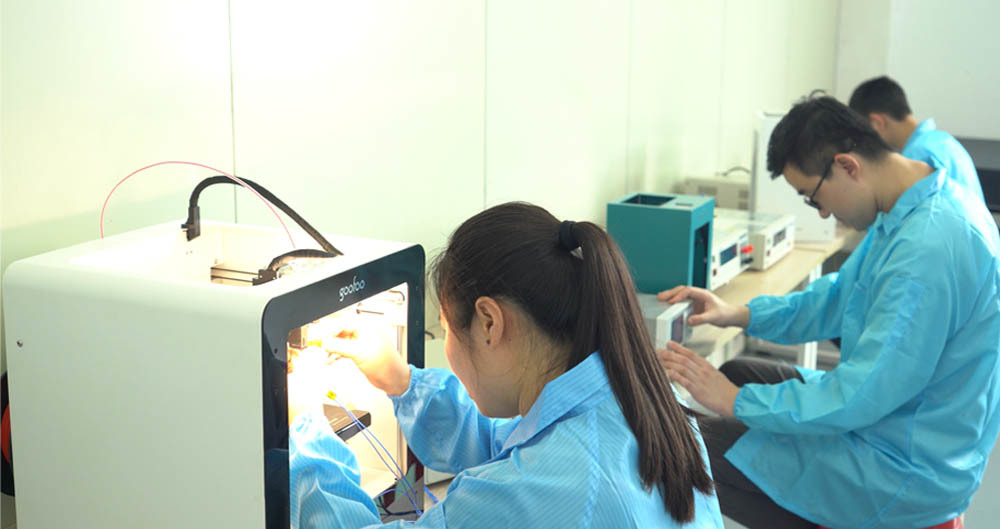
3D printing, known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that enables the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital files. This process has shifted the paradigm of product design and development, making it possible to bring ideas to life in ways previously deemed impossible. As industries worldwide embrace this technology, we explore its intricacies, applications, and the potential it holds for the future.
2. What is 3D Printing?
At its core, **3D printing** is a process of creating physical objects by layering materials based on a digital blueprint. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often involve cutting away material from a solid block, 3D printing adds material layer by layer, allowing for intricate designs and customized products. This process can utilize a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and even biological substances.
3. How Does 3D Printing Work?
The **3D printing process** generally involves the following stages:
3.1 Designing the Model
The journey begins with creating a digital model using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model serves as the blueprint for the object that will be printed.
3.2 Slicing the Model
Once the design is complete, it is converted into a format suitable for 3D printing. This involves "slicing" the model into thin horizontal layers, which the printer will build upon sequentially.
3.3 Printing the Object
The printer then takes the sliced model and begins the additive process. Depending on the 3D printing technology used—such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)—the printer applies the material in layers, gradually forming the final object.
3.4 Post-Processing
After printing, some objects require post-processing steps, such as removing support structures, sanding, or applying finishes to achieve the desired quality and appearance.
4. Applications of 3D Printing Across Industries
3D printing has found applications across various fields, revolutionizing the way products are designed and manufactured. Here, we explore some prominent industries leveraging this technology.
4.1 3D Printing in Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, **3D printing** is making significant strides. It is being used to create custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even bioprinting tissues and organs. This technology allows for personalized medical solutions that fit the unique needs of each patient.
4.2 3D Printing in Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies utilize 3D printing for rapid prototyping, tooling, and producing complex parts that would be challenging to create using traditional methods. This enhances efficiency and reduces costs associated with production.
4.3 3D Printing in Aerospace
The aerospace industry has embraced 3D printing for producing lightweight, high-strength components. This not only lowers fuel consumption but also allows for more complex geometries that enhance performance.
4.4 3D Printing in Automotive
Automotive manufacturers are incorporating 3D printing for everything from prototyping new designs to producing custom parts on-demand. This flexibility helps reduce inventory costs and speeds up the development cycle.
4.5 3D Printing in Fashion
Fashion designers are exploring the creative possibilities offered by 3D printing, producing unique garments and accessories that challenge traditional design boundaries. This technology allows for a new level of customization and innovation in fashion.
5. Benefits of 3D Printing
The advantages of 3D printing extend beyond just innovative design capabilities. Below are some key benefits:
5.1 Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing reduces waste and minimizes material costs by using only what is necessary to create an object. This results in lower overall production costs, particularly for small batch runs.
5.2 Customization
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing is its ability to produce customized products tailored to individual specifications without incurring high costs.
5.3 Speed of Production
The speed at which prototypes and products can be created allows businesses to accelerate their development timelines, bringing products to market faster than ever before.
5.4 Complex Designs
3D printing enables the production of intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
5.5 Sustainability
By reducing waste and allowing for localized production, 3D printing presents a more sustainable alternative to conventional manufacturing processes.
6. Challenges Facing 3D Printing
Despite its numerous benefits, 3D printing faces several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential.
6.1 Material Limitations
While advancements are being made, the range of materials suitable for 3D printing is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing processes.
6.2 Speed and Scalability
Though 3D printing is fast for prototyping, scaling up production to meet high-volume demands can be challenging and may not always be faster than traditional methods.
6.3 Quality Control
Ensuring consistent quality across printed products can be a challenge, particularly when using different machines or materials.
6.4 Intellectual Property Issues
The ease of copying designs raises concerns about copyright and intellectual property, presenting legal challenges for designers and companies.
7. The Future of 3D Printing
The future of **3D printing** appears promising, with ongoing advancements in materials, technology, and applications. As industries continue to explore innovative uses, we can expect to see:
7.1 Expansion into New Markets
As 3D printing technology evolves, it will likely penetrate new markets, including construction, food production, and even space exploration.
7.2 Enhanced Materials
Research into new materials and composites will expand the capabilities of 3D printing, allowing for stronger, more versatile products.
7.3 Integration with AI
Artificial Intelligence will play a significant role in optimizing 3D printing processes, enhancing efficiency, and enabling smarter design capabilities.
8. Conclusion
**3D printing** is more than just a technological marvel; it is a transformative force across various industries, reshaping how we think about design, production, and customization. As we continue to explore its potential, 3D printing promises to unlock new possibilities, enabling us to turn our ideas into reality with unprecedented speed and accuracy. The journey of 3D printing is just beginning, and as we embrace its capabilities, the impact on our world will be profound.
9. FAQs About 3D Printing
What materials can be used in 3D printing?
3D printing can utilize a variety of materials, including plastics (like PLA and ABS), metals (like titanium and aluminum), ceramics, and even biological materials for bioprinting.
How long does it take to 3D print an object?
The time required to print an object varies based on its size, complexity, and the specific 3D printing technology used. Small objects may take just a few hours, while larger, more complex designs can take several days.
Is 3D printing eco-friendly?
3D printing can be more environmentally friendly than traditional manufacturing by minimizing waste and allowing for localized production, reducing transportation emissions.
Can I 3D print food?
Yes, 3D printing technology is being explored in the food industry, with machines capable of printing edible ingredients to create intricate food designs.
What industries benefit most from 3D printing?
Industries such as healthcare, automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and fashion are significantly benefiting from the advances in 3D printing technology.
3d printer
Recommended News
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Skype / WhatsApp: +86 592-5713513 / +86-13860126490
No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong'an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Xiamen Goofoo Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备2022008070号-1 SEO 300.cn
Phone:+0086 592-5713513
Address: No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong’an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Email: sales@goofoo3d.com
We will give you feedback in time