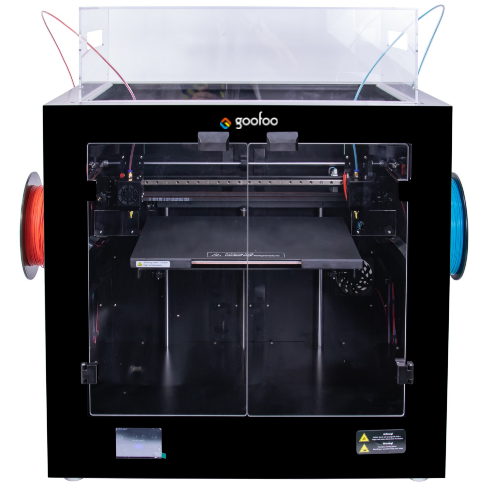
Revolutionizing Manufacturing with PLA 3D Printers: A Comprehensive Guide
2025-05-04 11:20
Revolutionizing Manufacturing with PLA 3D Printers
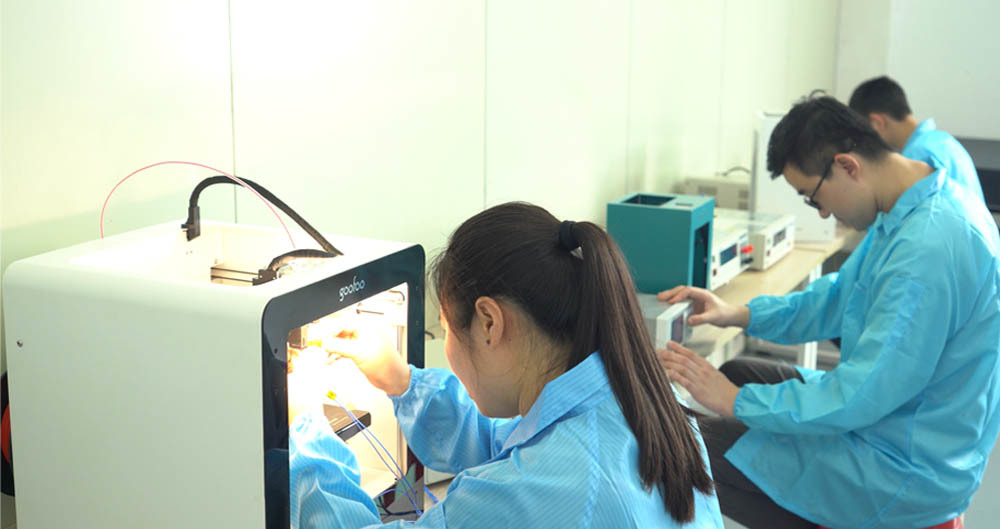
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, **PLA 3D printers** have emerged as transformative tools that not only enhance efficiency but also redefine design possibilities. As we delve into the world of 3D printing, particularly the use of **Polylactic Acid (PLA)**, we uncover how this biodegradable material is changing the way products are conceived and produced.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is PLA?
- 2. Advantages of PLA 3D Printing
- 3. Applications of PLA in Manufacturing
- 4. Impact on the Supply Chain
- 5. Environmental Benefits of PLA
- 6. Challenges and Limitations of PLA 3D Printing
- 7. The Future of PLA 3D Printing in Manufacturing
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is PLA?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a **biodegradable thermoplastic** derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is widely used in the **3D printing industry** due to its ease of use and minimal warping issues during the printing process. PLA is particularly favored for its **low melting temperature**, which allows for intricate designs to be achieved without the need for complex machinery.
Why Choose PLA?
PLA stands out among various filament options in 3D printing due to its **user-friendly characteristics**. Suitable for both beginners and experienced users, PLA provides a smooth printing experience. Moreover, its non-toxic nature makes it a safe choice for classroom and home environments. With a wide array of colors and finishes available, PLA also facilitates creative expression in design.
2. Advantages of PLA 3D Printing
The rise of **PLA 3D printing** is attributed to numerous advantages that it offers to manufacturers:
Cost-Effective Production
One of the primary benefits of using PLA in 3D printing is its cost-effectiveness. The material is relatively inexpensive compared to other filaments, allowing manufacturers to lower their production costs while maintaining quality. This is especially crucial for small businesses looking to innovate without breaking the bank.
Enhanced Design Flexibility
PLA filaments provide manufacturers with **design flexibility** that traditional manufacturing methods often cannot match. With 3D printing, complex geometries that were once challenging to produce can be easily executed. This enables **rapid prototyping**, allowing for quick iterations and improvements in product design.
Speed of Production
3D printing with PLA materials allows for fast production times. As parts can be printed directly from digital designs, there is **no need for time-consuming setups** typical in traditional manufacturing processes. This speed can significantly reduce time to market for new products.
3. Applications of PLA in Manufacturing
PLA 3D printers are making significant inroads across various sectors, including:
Consumer Products
From toys to household items, PLA is widely used in producing consumer goods. Its aesthetic appeal and adaptability make it a preferred choice for manufacturers striving to create innovative products that meet consumer demands.
Aerospace and Automotive
In the aerospace and automotive industries, PLA is utilized for producing prototypes of components. The ability to create lightweight, intricate parts can lead to performance enhancements and fuel efficiency, making it a valuable asset in these sectors.
Healthcare
In healthcare, PLA's biocompatibility allows for the creation of medical models and instruments. Surgeons can use these precise replicas for practice, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes. Furthermore, PLA is being explored for use in bio-printing and prosthetics.
4. Impact on the Supply Chain
Adopting PLA 3D printing technology can drastically alter the supply chain dynamics in manufacturing. Here are some key impacts:
On-Demand Production
With the ability to produce parts on-demand, companies can significantly reduce inventory costs. This shift allows manufacturers to respond more quickly to market demands and reduces the risks associated with overproduction.
Local Manufacturing
By leveraging PLA 3D printing, businesses can shift towards **local manufacturing**, minimizing shipping costs and lead times. This decentralization can also enhance sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
5. Environmental Benefits of PLA
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is a significant concern, and PLA 3D printing offers several advantages:
Biodegradability
Unlike traditional petroleum-based plastics, PLA is biodegradable, breaking down into natural components under industrial composting conditions. This characteristic can help manufacturers reduce their **environmental impact**.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Since PLA is derived from renewable resources, its production can result in a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional manufacturing methods. Additionally, the potential for local production further minimizes emissions linked to transportation.
6. Challenges and Limitations of PLA 3D Printing
Despite its advantages, PLA 3D printing is not without challenges:
Heat Resistance
One significant limitation of PLA is its low heat resistance. It can deform when exposed to high temperatures, making it unsuitable for applications requiring durability under heat.
Mechanical Properties
While PLA is strong for many applications, it is not the most robust choice for parts requiring high mechanical strength. Manufacturers may need to consider alternative materials for such uses.
7. The Future of PLA 3D Printing in Manufacturing
The future of PLA 3D printing in manufacturing looks promising, with advancements in technology paving the way for broader applications:
Innovative Developments
Ongoing research into enhancing the properties of PLA, such as improving its heat resistance and mechanical strength, could expand its usability in various sectors. Innovations in **blending PLA with other materials** may yield stronger, more versatile filaments.
Integration with Industry 4.0
The integration of PLA 3D printing with **Industry 4.0** technologies, such as IoT and AI, could revolutionize manufacturing processes. Smart factories that utilize real-time data for optimizing production could lead to unprecedented efficiencies and reduced waste.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lifespan of PLA products?
The lifespan of PLA products varies based on environmental conditions. In optimal conditions, PLA can last for several months to a few years, but it may degrade faster in composting settings.
Can PLA be recycled?
PLA is technically recyclable, but not all recycling facilities accept it. It is best to check with local waste management programs to confirm their capabilities.
Is PLA safe for food contact?
PLA is generally considered safe for food contact, but it is essential to ensure that the specific filament used is certified for such applications to avoid any health risks.
How does PLA compare to other 3D printing materials?
PLA is easier to print and more environmentally friendly than many other materials like ABS. However, it may not offer the same durability and heat resistance as some alternatives.
What industries are adopting PLA 3D printing technology?
Industries such as consumer products, aerospace, automotive, and healthcare are increasingly adopting PLA 3D printing technology due to its benefits in **speed, cost, and sustainability**.
Conclusion
In conclusion, **PLA 3D printers** are transforming the manufacturing landscape, offering cost-effective, flexible, and environmentally friendly solutions. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for PLA to revolutionize various industries becomes increasingly apparent. Manufacturers looking to innovate and stay competitive should consider the myriad advantages that PLA 3D printing brings to modern production.
pla 3d printer
Recommended News
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Skype / WhatsApp: +86 592-5713513 / +86-13860126490
No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong'an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Xiamen Goofoo Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备2022008070号-1 SEO 300.cn
Phone:+0086 592-5713513
Address: No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong’an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Email: sales@goofoo3d.com
We will give you feedback in time