From Concept to Creation: The Art and Science of 3D Printer Design
2025-09-17 12:20
From Concept to Creation: The Art and Science of 3D Printer Design
Table of Contents
- Understanding 3D Printing Technology
- The Design Process: From Idea to Prototype
- Key Components of 3D Printers: Anatomy of a Machine
- Materials Used in 3D Printing: Choosing the Right Filament
- Software for 3D Printing: Designing Your Model
- Trends in 3D Printing Technology: The Future is Here
- Applications of 3D Printing: Revolutionizing Industries
- Challenges in 3D Printer Design: Overcoming Obstacles
- Conclusion
- FAQs about 3D Printer Design
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, refers to the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This technology has transformed the way we conceptualize and produce items, enabling designers and engineers to explore complex geometries, reduce material waste, and streamline production processes. By layering materials, 3D printers construct objects from the ground up, making it possible to create intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing techniques.
The Design Process: From Idea to Prototype
Ideation and Concept Development
Every successful 3D printer design begins with ideation—a creative brainstorming phase where concepts are generated. Designers consider functionality, aesthetics, and user needs. Sketching ideas or creating mood boards can help visualize these concepts. The goal at this stage is to develop a clear vision and identify the target audience for the 3D printed object.
Creating Digital Models
Once the concept is solidified, designers transition to creating digital models using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This stage involves translating ideas into a 3D digital format that can be understood by printers. Different CAD tools offer robust features to facilitate intricate designs, making it crucial to choose the right software that aligns with the project requirements and the designer’s expertise.
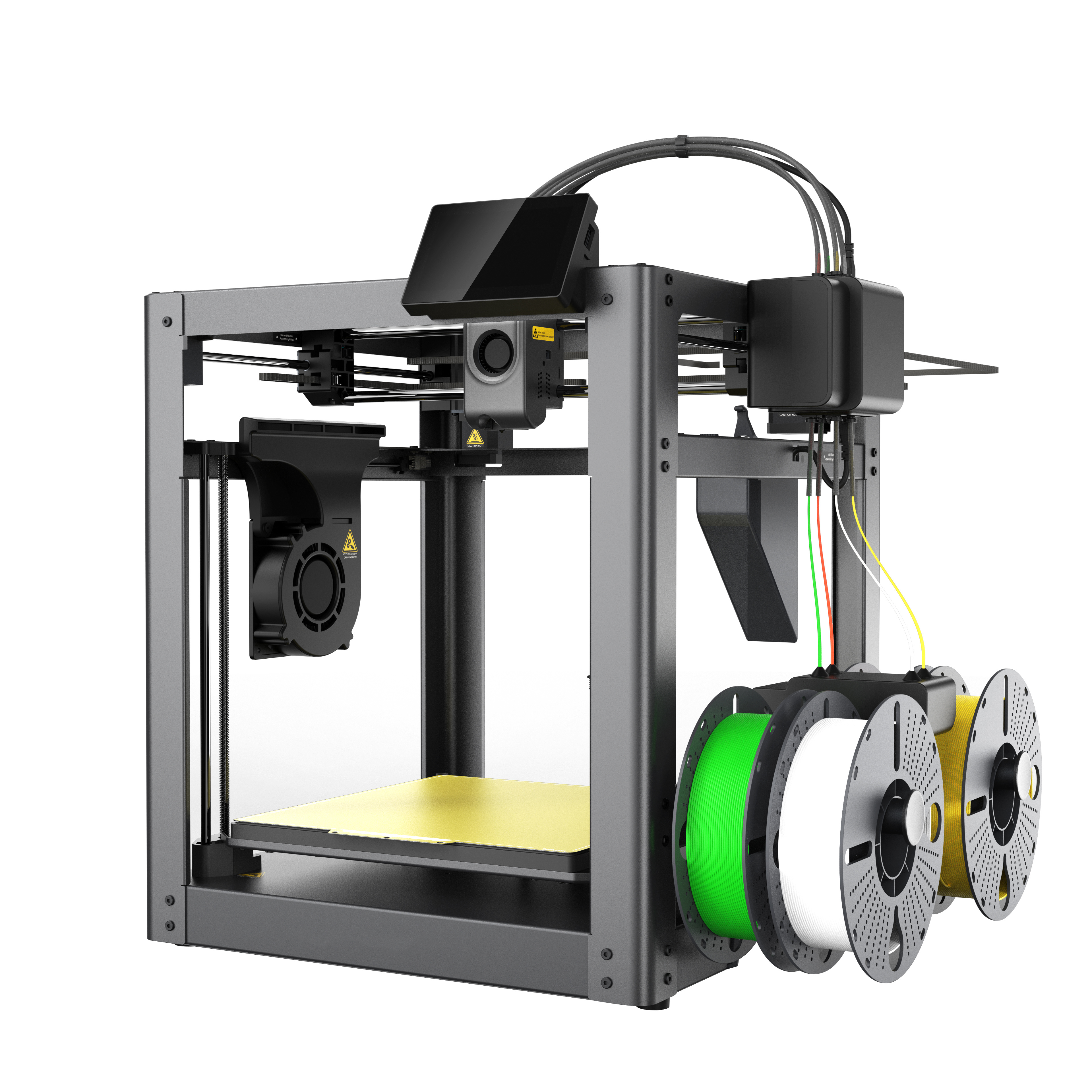
Key Components of 3D Printers: Anatomy of a Machine
Print Head
The print head is a critical component that extrudes the filament during the printing process. It needs to be precisely calibrated to ensure consistent material flow, temperature control, and movement along the X, Y, and Z axes. Advanced models may have multiple print heads to enable multi-material printing or dual-color designs.
Build Platform
The build platform is where the object is created layer by layer. It can be heated or non-heated, affecting adhesion and the quality of the final print. A heated build platform helps reduce warping, especially with materials like ABS. Ensuring proper leveling of the build platform is essential for achieving a successful print.
Movement System
The movement system comprises motors and belts that enable the print head and build platform to move accurately. Stepper motors are commonly used in 3D printers due to their precision and reliability. Smooth movement is crucial for achieving fine details and maintaining consistent layer heights.
Materials Used in 3D Printing: Choosing the Right Filament
The choice of materials significantly impacts the performance and durability of 3D printed objects. Common materials include:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): Ideal for beginners, PLA is easy to print and biodegradable.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its strength and heat resistance, ABS is widely used for functional parts.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Combining durability with flexibility, PETG is suitable for various applications.
- Nylon: Renowned for its toughness and flexibility, nylon is ideal for high-performance parts.
Software for 3D Printing: Designing Your Model
Popular CAD Software
Several CAD software options cater to different skill levels and project needs. Popular choices include:
- TinkerCAD: A user-friendly platform for beginners.
- Fusion 360: A powerful tool for professionals offering parametric design capabilities.
- Blender: Excellent for artistic designs and modeling.
Slicing Software
Once the design is complete, slicing software translates the 3D model into a format that the printer can understand, generating the necessary G-code. Popular slicing programs include Cura, PrusaSlicer, and Simplify3D. These tools allow users to adjust print settings, such as layer height, print speed, and infill density, which can significantly impact the final product’s quality.
Trends in 3D Printing Technology: The Future is Here
Advancements in Materials
The development of new materials continues to expand the possibilities of 3D printing. Innovations in bioprinting, where living cells are used, and composite materials that combine various properties for enhanced performance are paving the way for cutting-edge applications across industries.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into the design and printing processes. These technologies can optimize printing paths, predict potential failures, and enhance overall efficiency, making the process smarter and more reliable.
Applications of 3D Printing: Revolutionizing Industries
Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, 3D printing is making waves with custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even bioprinted tissues. Surgeons can create patient-specific models for preoperative planning, improving surgical outcomes and patient care.
Aerospace and Automotive
The aerospace and automotive industries utilize 3D printing for rapid prototyping and manufacturing lightweight components. This not only accelerates the design process but also enhances fuel efficiency and performance.
Challenges in 3D Printer Design: Overcoming Obstacles
Quality Control
Maintaining consistent quality in 3D printing can be challenging due to variations in materials and environmental conditions. Rigorous testing and calibration are essential to ensure that printers perform optimally and that the final products meet quality standards.
Cost Management
While the upfront cost of 3D printers has decreased, managing operational costs remains a challenge. Factors such as material costs, maintenance, and energy consumption must be carefully considered to ensure the sustainability of 3D printing operations.
Conclusion
The journey from concept to creation in 3D printer design is a fascinating blend of art and science. Understanding the intricacies of design, technology, and materials allows creators to unlock the full potential of 3D printing. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of revolutionizing various industries, offering innovative solutions to complex problems, and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in manufacturing and design.
FAQs about 3D Printer Design
1. What is the best material for a beginner in 3D printing?
PLA is often recommended for beginners due to its ease of use, low warping, and non-toxic nature.
2. How long does it take to print a 3D object?
The time required to print a 3D object varies based on its size, complexity, and the settings used on the printer. It can range from a few minutes to several hours.
3. Can I use multiple materials in one print?
Yes, some advanced 3D printers allow for multi-material printing, enabling the creation of complex objects with different properties.
4. What are the common issues encountered during 3D printing?
Common issues include warping, layer separation, and misalignment. Proper calibration and settings adjustments can help mitigate these problems.
5. How can I improve the quality of my prints?
Improving print quality can be achieved through regular maintenance, proper calibration, and experimenting with print settings such as speed, temperature, and layer height.
3d printer design
Recommended News
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Skype / WhatsApp: +86 592-5713513 / +86-13860126490
No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong'an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Xiamen Goofoo Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备2022008070号-1 SEO 300.cn
Phone:+0086 592-5713513
Address: No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong’an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Email: sales@goofoo3d.com
We will give you feedback in time