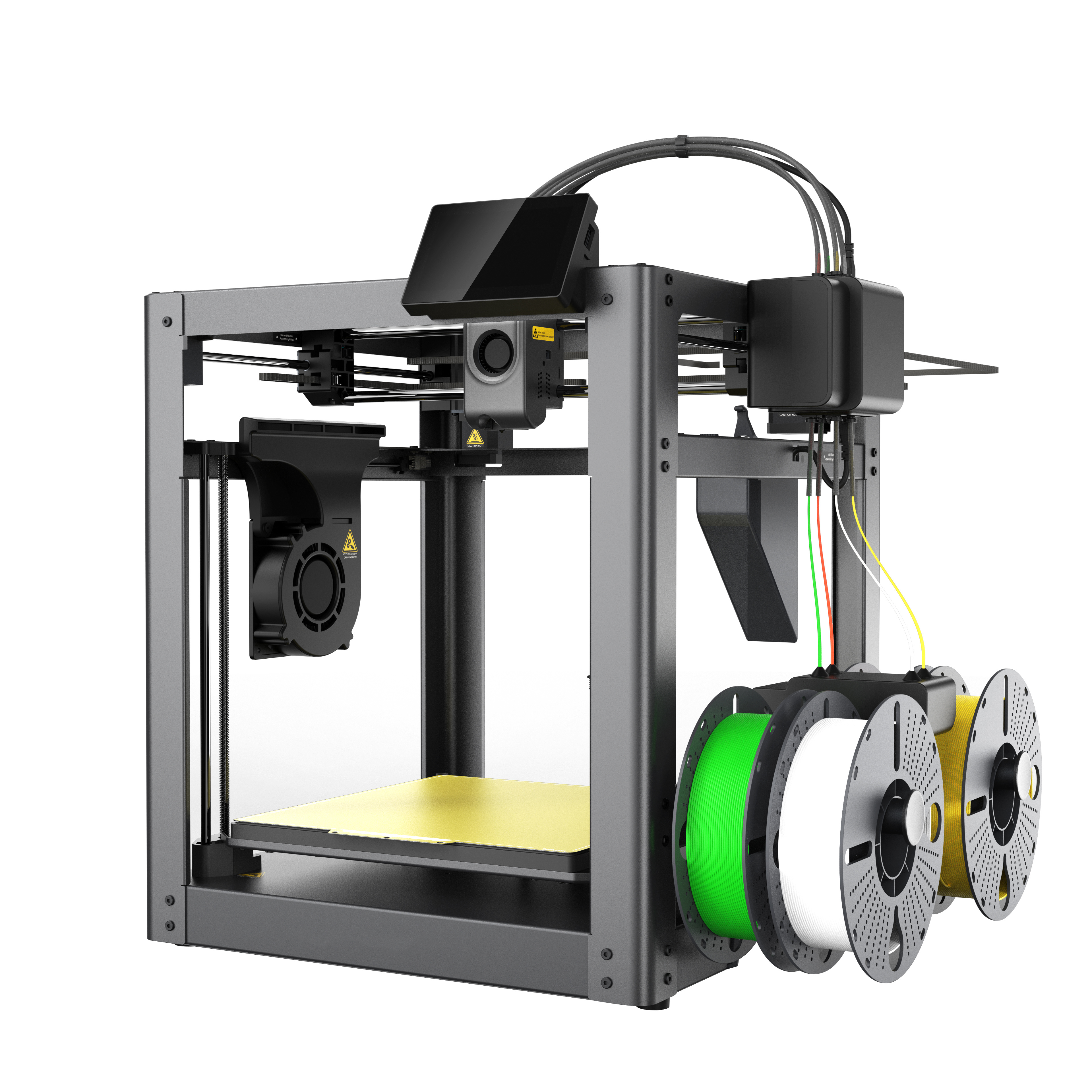
Elevate Your Prototyping Game with Ender 3D Printer Precision
2025-09-09 13:40
Elevate Your Prototyping Game with Ender 3D Printer Precision
Table of Contents
- What is the Ender 3D Printer?
- Key Features and Advantages of the Ender 3D Printer
- How to Set Up Your Ender 3D Printer
- Choosing the Right Materials for Your 3D Prints
- Best Practices for Achieving Precision in Prototyping
- Applications of the Ender 3D Printer in Prototyping
- Troubleshooting Common Issues with Ender 3D Printers
- The Future of 3D Printing Technology and the Ender Series
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is the Ender 3D Printer?
The Ender 3D printer is a versatile and user-friendly 3D printing machine that has gained popularity among hobbyists and professionals alike. Designed by Creality, this printer is known for its reliability and precision, making it an excellent choice for anyone looking to create detailed prototypes or models. With an open-source design, it allows for extensive customization, catering to users' varying needs and preferences.
Key Features and Advantages of the Ender 3D Printer
The Ender 3D printer boasts a host of features that contribute to its reputation as a leading choice for 3D printing:
1. High Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout aspects of the Ender 3D printer is its ability to produce high-quality prints with exceptional precision. Thanks to its advanced stepper motors and precise control systems, it can achieve layer resolutions as fine as 0.1 mm. This level of accuracy ensures that your prototypes are not only functional but also visually appealing.
2. Affordable Pricing
Affordability is a significant factor for many users when selecting a 3D printer. The Ender 3D printer offers an excellent balance of price and performance, making it accessible for beginners and professionals alike. With its low initial investment, users can dive into the world of 3D printing without breaking the bank.
3. Easy Assembly and Setup
The Ender 3D printer comes partially assembled, allowing users to set it up quickly and without hassle. Detailed instructions guide you through the assembly process, enabling you to start printing in no time. Its intuitive interface makes it easy to navigate through settings and customize prints.
4. Compatibility with Various Filaments
Another advantage of the Ender 3D printer is its compatibility with multiple filament types. Whether you prefer PLA, ABS, PETG, or TPU, this printer can handle it all. This versatility opens up a world of possibilities for your prototyping projects, allowing you to experiment with different materials and finishes.
5. Community Support and Resources
The Ender 3D printer has a vibrant online community that offers extensive support for users. From troubleshooting tips to advanced modifications, you can find a wealth of resources and advice from fellow enthusiasts. This sense of community fosters a collaborative environment, helping you refine your skills and enhance your printing experience.
How to Set Up Your Ender 3D Printer
Setting up your Ender 3D printer is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to get started:
Step 1: Unboxing and Assembly
Carefully unbox your printer and familiarize yourself with all components. Follow the assembly instructions to piece together the frame, build plate, and extruder. Most users can complete the assembly in under an hour.
Step 2: Level the Print Bed
Proper bed leveling is crucial for achieving successful prints. Adjust the print bed to ensure it is level across all corners. This will help to maintain consistent adhesion and improve print quality.
Step 3: Load the Filament
Once the printer is assembled and the bed is leveled, load your chosen filament into the extruder. Make sure to preheat the printer to the appropriate temperature for the filament type you are using.
Step 4: Prepare Your First Print
Select a test model from your slicing software and start your first print. Monitor the printing process closely, especially during the initial layers, to ensure everything is functioning properly.
Choosing the Right Materials for Your 3D Prints
Understanding the various types of materials available for 3D printing is essential for achieving the best results with your Ender 3D printer. Here’s a breakdown of some popular filament options:
1. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is one of the most commonly used filaments due to its ease of use and low printing temperature. It’s biodegradable and available in a variety of colors, making it ideal for prototypes and decorative items.
2. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a sturdy filament known for its durability and impact resistance. It’s suitable for functional prototypes but requires a heated bed for optimal adhesion and to minimize warping.
3. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
PETG combines the best features of PLA and ABS, offering strength, flexibility, and ease of printing. It’s resistant to moisture and chemicals, making it a great choice for practical applications.
4. TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
TPU is a flexible filament that can be used to create soft, rubber-like prints. It’s perfect for prototypes requiring elasticity and durability, such as phone cases or wearable designs.
Best Practices for Achieving Precision in Prototyping
To maximize the precision and quality of your 3D prints, consider adopting the following best practices:
1. Optimize Print Settings
Experiment with various print settings in your slicing software, such as layer height, print speed, and infill density. Optimizing these parameters can significantly impact the final quality of your prints.
2. Maintain Your Printer
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your Ender 3D printer operates smoothly. Keep the print bed clean, check for wear on the nozzle, and lubricate moving parts as needed to ensure longevity and precision.
3. Monitor Temperature Settings
Different materials require different temperature settings, both for the nozzle and the heated bed. Make sure to refer to the filament manufacturer's recommendations and adjust accordingly to prevent issues like warping or stringing.
4. Use Quality Filament
Investing in high-quality filament can make a noticeable difference in print quality. Cheap filaments may lead to inconsistent results and increase the likelihood of clogs or failures during printing.
Applications of the Ender 3D Printer in Prototyping
The Ender 3D printer is suitable for a wide range of applications, making it an invaluable tool for designers and engineers:
1. Product Design and Prototyping
Engineers and product designers often use the Ender 3D printer to create prototypes of their concepts. Rapid prototyping allows for quick iterations, enabling designers to test and refine their ideas effectively.
2. Education and Training
In educational settings, the Ender 3D printer serves as a valuable tool for teaching students about design, engineering principles, and manufacturing processes. It fosters creativity and problem-solving skills in a hands-on environment.
3. Art and Sculptures
Artists utilize the Ender 3D printer to create intricate sculptures and artistic pieces. With its precision capabilities, it allows for the creation of detailed designs that push the boundaries of traditional art methods.
4. Functional Parts and Prototypes
The ability to create functional parts with the Ender 3D printer opens up opportunities for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. Prototyping functional components accelerates the product development process.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Ender 3D Printers
Even experienced users may encounter issues during the printing process. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
1. Poor Bed Adhesion
If prints aren’t sticking to the bed, consider re-leveling the bed or using an adhesive like glue stick or hairspray. Ensuring the surface is clean can also improve adhesion.
2. Stringing
Stringing occurs when filament oozes from the nozzle during travel moves. To reduce stringing, increase the retraction distance, lower the printing temperature, or enable a feature called “combing” in your slicing software.
3. Layer Separation
Layer separation can happen due to insufficient adhesion between layers. Increase the printing temperature or check the flow rate settings in your slicing software to ensure the filament is being extruded properly.
4. Clogged Nozzle
If your printer fails to extrude filament, the nozzle may be clogged. Clean the nozzle using a needle or by performing a cold pull with the filament to remove any debris.
The Future of 3D Printing Technology and the Ender Series
The world of 3D printing is rapidly evolving, and the Ender series is at the forefront of this innovation. As technology advances, we can expect:
1. Enhanced Materials
New filament materials with improved properties are continually being developed, enabling users to create even more complex and functional prototypes.
2. Improved Printing Speed
Future iterations of the Ender 3D printer are likely to feature faster printing speeds while maintaining high-quality output, significantly reducing production times for prototypes.
3. Advanced Automation
Integration of AI and automation technology could streamline the printing process, allowing for more efficient monitoring and adjustments of print settings in real-time.
4. Broadened Accessibility
As 3D printing becomes more mainstream, we can anticipate increased accessibility for educational institutions and small businesses, democratizing prototyping and manufacturing processes worldwide.
Conclusion
The Ender 3D printer stands out as a powerful tool for anyone looking to elevate their prototyping game. With its precision, affordability, and versatility, it caters to a wide range of applications, from product design to art. By following best practices and leveraging community resources, users can unlock the full potential of this remarkable technology. As 3D printing continues to evolve, embracing these advancements will further enhance the capabilities and applications of the Ender series, making it an indispensable asset for innovators and creators alike.
FAQs
1. What is the print volume of the Ender 3D printer?
The Ender 3D printer typically has a print volume of 220 x 220 x 250 mm, providing ample space for most prototyping projects.
2. Is the Ender 3D printer suitable for beginners?
Yes, the Ender 3D printer is user-friendly and comes with detailed assembly instructions, making it a great choice for beginners.
3. What types of filament can I use with the Ender 3D printer?
The Ender 3D printer supports multiple filament types, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU.
4. How do I avoid warping in my prints?
To minimize warping, ensure proper bed leveling, use a heated bed, and select the appropriate temperature settings for your chosen filament.
5. Can I upgrade my Ender 3D printer?
Yes, the Ender 3D printer is highly customizable, and many users choose to upgrade components like the hotend, bed, and cooling system to enhance performance.
ender 3d printer
Recommended News
 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Skype / WhatsApp: +86 592-5713513 / +86-13860126490
No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong'an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Xiamen Goofoo Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved 闽ICP备2022008070号-1 SEO 300.cn
Phone:+0086 592-5713513
Address: No.88-3, North Tongji Road, Xike County, Tong’an District, Xiamen, Fujian China
Email: sales@goofoo3d.com
We will give you feedback in time